What is the Lean Startup Methodology? – Pillars, and More
Table of Contents
What is the Lean Startup Methodology?
The Lean Startup methodology approaches business and product launches based on validated learning, scientific experimentation, and iteration in product launches. This method can shorten development cycles, measure progress, and gain valuable feedback from customers.
Thus, companies that apply the Lean Startup methodology, especially startups, can design their products or services to meet the demand of their customer base without requiring large amounts of initial financing or huge investments to launch a product.
Eric Ries developed the Lean Startup concept in 2008 in his book ” The Lean Startup Method: How to Create Successful Companies Using Continuous Innovation.” At first, the method creates for high-tech companies. Still, over time it has been extended to other sectors, applying to any individual, group, or company that needs to introduce new products and services to the market.
What are the Pillars of the Lean Startup Methodology?
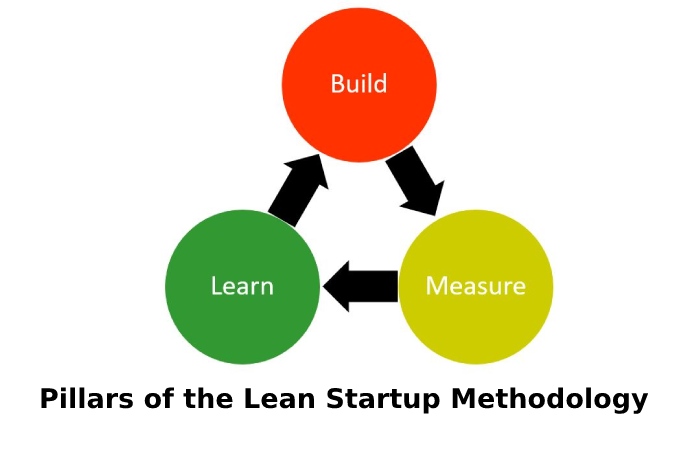
The Lean Startup methodology base on meeting the consumer’s specific needs and knowing how to do it using the minimum amount of resources.
The method developed by Ries puts the eye on previous research, on discovering what needs the customer has and what output the products to manufacture may have. By knowing what the client needs, startups stop investing in production processes. Or innovations that are not in the client’s interest, that the client does not request, and, therefore, do not have space in the market.
Ries suggests that recently started companies, startups, stop operating blindly and start acting based on what they expect and what customers want, not so much on happy ideas from entrepreneurs but not validated by the market.
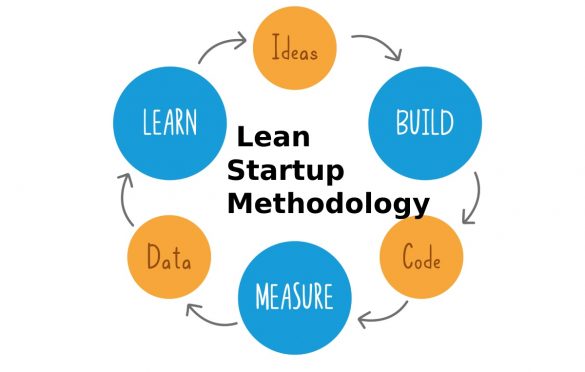
The Lean Startup method focuses on three steps set in an endless and constantly moving circle: It begins by creating a product, continues by measuring the results of what makes, and continues with learning what is estimated to start creating again.
1. Build
When launching a startup, there is insufficient market data to create a product wholly adjusted to the potential client’s needs. Faced with this initial hesitant phase, the need arises to make what you want and put this product on the market.
It isn’t easy to have a completed final product. The ideal is to create the minimum viable product (MVP, in its acronym in English) with enough characteristics to make it known in the market. Without ultimately completing it, this product collects data, learns what improvements to implement, and creates the typical consumer.
The minimum viable product concept launched by Ries is necessary to begin collecting data and measuring results. This product model does not seek to be the final result but rather an excellent product to test the potential customer’s reaction.
With evident product characteristics, it is possible to narrow down a potential product customer better. This is one of the most critical axes: the minimum viable product will also help to define which customers may be the ones who buy the product that finally launches on the market.
2. Measure
When creating a new product for the market, developing a reliable and efficient measurement method is essential. It is necessary to evaluate the company’s data, the means available, or the expected expenses, for example. Being clear about what is available and expectations can be a fundamental step to a successful product.
The second step of the Lean Startup methodology proposes that the needs of potential clients are measured so that the product adjusts to what they expect or want.
Knowing the internal product (the company itself) and the external product (what customers expect and want) makes it possible to develop the final product to reach the market.
3. Learn
The third axis of the Lean Startup methodology is that the company learns from the data collected and the product itself created. It bases on learning firsthand from the experience of having made the product and knowing the market’s needs.
In addition, it is interesting that what you learn serves to start the process again. Since this acquired knowledge must apply to a new approach that begins again. A product re-creates, which will be an improvement, forms the circle of creating, measuring, and learning again.
The importance of the MVP in the Lean Startup Methodology cycle understand as:
- Avoid making the mistake of creating a product that nobody wants, something prevalent in the past of many startups. The idea is that the product solves a real problem, and users are willing to pay for it.
- It allows testing and obtaining evidence about the product and the market before it is too late for the startup.
- Maximize customer learning with minimal investment.
Advantages of the Lean Startup Methodology
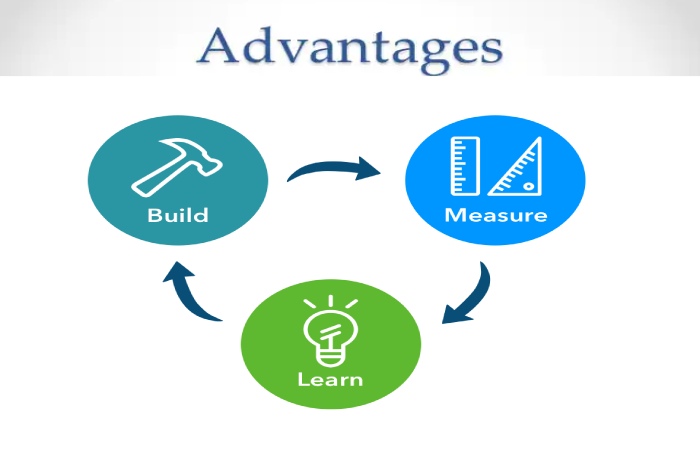
The Lean Startup methodology allows validated learning, that is, to understand as quickly as possible what customers want and apply it to optimize the product development cycle. In this way, both the terms and potential financing needs reduce.
Some of the advantages that can achieve using this method are:
- It eliminates the risk of spending a lot of money on developments that do not make sense because the market, for whatever reason, does not need them or, at least, is not willing to consume them.
It helps to structure innovative ideas and appropriately. For this, decisions are made with data in hand and not with personal impressions. - Make sure you have a minimum viable product that meets the basic needs of a typical customer.
- Reduces the failure rate of a startup.
- The Lean Startup model helps eliminate inefficient practices from many startups. For this reason, the methodology focuses on increasing the value of the company’s production in those aspects. And techniques that raise the cost of production eliminate. Therefore, the Lean Startup model seeks. Companies can have more opportunities to succeed without the need for large budgets, elaborate business plans, or a perfect product.
- The model designed by Ries focuses on the customer, who becomes an essential and fundamental element in developing the product. The customer’s efforts will not create a product that they do not want, but instead, their money invests in the final product, the one they want to buy.
Do you Dare with the Lean Startup Methodology?
Now that you know the steps of the lean startup, we encourage you to try applying them in your company. It will make you go faster and be more agile.
If you need to expand your knowledge regarding the method, we leave you some books. It will solve possible doubts and make your steps firmer. For instance:
The Lean Startup method: How to create successful companies using continuous innovation.
The Lean Startup: How Constant Innovation Makes Radically Successful Businesses.
LEAN Customer Development: How to create the products that your customers will buy.
Design thinking for strategic innovation.
And if you want to go further and learn with a 100% online methodology, in a practical way. And have classes to solve all your doubts, we 100% recommend the Design Thinking and Lean Startup Course. Find out how to get started with companies like Mercadona Tech and Mango.
Conclusion
The Lean Startup methodology, a concept that Eric Ries developed in 2008 in his work “The Lean Startup method: How to create successful companies using continuous innovation.” Aims to reduce time and cost when creating a company, startup, or product.
Also Read: Choose The Word Which Is Different From The Rest-Breif Summary Report
Related Searches to Lean Startup Methodology
[lean startup methodology pdf]
[lean startup methodology examples]
[lean startup fases]
[the order of the circuit of the lean startup methodology is]
[methodology lean startup steps]
[lean start-up methodology]
[the number of fundamental elements of the lean startup methodology is]
[lean startup definition]
[lean startup examples]
[lean startup meaning]
[lean startup build-measure-learn]
[lean startup ideas]
[lean startup principles]
[the lean startup pdf]
[lean startup methodology pdf]
[lean startup summary]


